Which Bacterium Causes Typhus?
Typhus is caused by several species of Rickettsia bacteria and it is important not to confuse it with typhoid fever, which is a severe infection caused by Salmonella bacteria.
The disease typhus is actually several closely related diseases, which differ by the species of bacteria that cause them and also by the insect host that transmits them to humans. Epidemic typhus, the most common type, is caused by Rickettsia prowazekii and is introduced into the human body by the bite of human lice. The bacteria live inside the digestive system of the lice and enter the bloodstream of people when the lice insert their mouth parts to feed.
The two other types of typhus are murine typhus and scrub typhus, Murine typhus is caused by the bacterium Rickettsia typhi and, as its name suggests, is transmitted by fleas that normally live on rats and mice, but that can bite and infect humans. Scrub typhus is caused by a different bacterial species, Orienta tsutsugamushi, which is transmitted by harvest mites that live on both humans and mice and rats. This last form of typhus is usually called spotted fever.
What is Typhus?
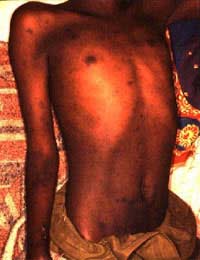
Typhus is an illness caused by infections of the bacteria mentioned already. The name comes from the Greek word 'typhos', which means hazy and has been used to describe the disease, because this leads to a hazy state of mind in those affected. Mental processes become impaired, leading to delirium and stupor, because of the high fever that the bacterial infection causes, up to 106 degrees Fahrenheit. The fever is very difficult to shake off and commonly persists for about two weeks. The person with typhus feels generally very ill with headache and other aches, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and a dry cough. They may also develop a rash, which is a dull red spreading rash on the torso.The infection starts with the bite of an insect vector, which can be sore, but other symptoms generally do not start to appear for about 3 weeks. The fever begins suddenly and the original bite becomes ulcerated and scabs over. The lymph nodes nearest to the bite area also become swollen and the symptoms worsen for a period of 2 weeks. Typhus can be fatal, but if someone does recover naturally, this process may take a further three weeks.

Re: What is C Difficile?
Kak esehiko sminor k112 typesofbacteria.co.uk
Re: What is C Difficile?
"Julia's Garland" (fr. Guirlande de Julie)
Re: Friendly Bacteria in the Digestive System
hello, thankyou for this website it was very helpful
Re: Friendly Bacteria in the Digestive System
nope im leaving now goodbye , mumm! crimble crumble ready?
Re: Friendly Bacteria in the Digestive System
The meat out of the bin is perfectly fine jackie!
Re: Friendly Bacteria in the Digestive System
Yeahhh jim not the right time were quite busy at the moment
Re: How Can People Catch Lyme Disease?
My symptoms of Lyme disease occurred in 2017, but was diagnosed in 2019. I had severe symptoms ranging from headache,…
Re: Friendly Bacteria in the Digestive System
kids
Re: Friendly Bacteria in the Digestive System
i like kids
Re: Friendly Bacteria in the Digestive System
I have yo kidz. i have the basement kids